ServiceManager 启动和获取(Native 层),源码基于 android-12.1.0
相关代码路径:
之所以从 servicemanager开始分析,是因为他比较特殊,即是 Client 和 Server 通信的中间人,Client 要先去servicemanager中寻找 Server 的 Binder 地址,同时也是一个特殊的 Server 端,作为一个特殊的 Server,他的功能很单一,就是返回指定 Server 的 Binder 地址。
1. servicemanager 启动注册 system/core/rootdir/init.rc
1 2 3 4 5 on init # Start essential services. start servicemanager start hwservicemanager start vndservicemanager
frameworks/native/cmds/servicemanager/servicemanager.rc
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 service servicemanager /system/bin/servicemanager class core animation user system group system readproc critical // 说明 servicemanager 是系统中的关键服务,关键服务是不会退出的,如果退出了,系统就会重启 onrestart restart apexd onrestart restart audioserver onrestart restart gatekeeperd onrestart class_restart main onrestart class_restart hal onrestart class_restart early_hal writepid /dev /cpuset /system -background /tasks shutdown critical
servicemanager 的源码入口在 frameworks/native/cmds/servicemanager/main.cpp
main.cpp.main()
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 int main (int argc, char ** argv) ... const char * driver = argc == 2 ? argv[1 ] : "/dev/binder" ; sp<ProcessState> ps = ProcessState::initWithDriver (driver); ps->setThreadPoolMaxThreadCount (0 ); ps->setCallRestriction (ProcessState::CallRestriction::FATAL_IF_NOT_ONEWAY); sp<ServiceManager> manager = sp<ServiceManager>::make (std::make_unique <Access>()); if (!manager->addService ("manager" , manager, false , IServiceManager::DUMP_FLAG_PRIORITY_DEFAULT).isOk ()) { LOG (ERROR) << "Could not self register servicemanager" ; } IPCThreadState::self ()->setTheContextObject (manager); ps->becomeContextManager (nullptr , nullptr ); sp<Looper> looper = Looper::prepare (false ); BinderCallback::setupTo (looper); ClientCallbackCallback::setupTo (looper, manager); while (true ) { looper->pollAll (-1 ); } return EXIT_FAILURE; }
主要做了三件事:
ProcessState::initWithDriver(driver):打开并初始化驱动设备;
ps->becomeContextManager(nullptr, nullptr):把 servicemanager 注册到驱动,成为 Binder 管理员(即设置为大管家),handle 是 0;
looper->pollAll(-1):进入循环等消息;
1.1 打开驱动,内存映射 frameworks/native/libs/binder/ProcessState.cpp
initWithDriver(driver)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 sp<ProcessState> ProcessState::initWithDriver (const char * driver) return init (driver, true ); } sp<ProcessState> ProcessState::init (const char *driver, bool requireDefault) ... [[clang::no_destroy]] static std::once_flag gProcessOnce; std::call_once (gProcessOnce, [&](){ ... std::lock_guard<std::mutex> l (gProcessMutex); gProcess = sp<ProcessState>::make (driver); }); ... return gProcess; }
创建一个 ProcessState 对象,参数 driver 值是 /dev/binder
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 #define BINDER_VM_SIZE ((1 * 1024 * 1024) - sysconf(_SC_PAGE_SIZE) * 2) ProcessState::ProcessState (const char *driver) : mDriverName (String8 (driver)) , mDriverFD (open_driver (driver)) , mVMStart (MAP_FAILED) , mThreadCountLock (PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER) , mThreadCountDecrement (PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER) , mExecutingThreadsCount (0 ) , mWaitingForThreads (0 ) , mMaxThreads (DEFAULT_MAX_BINDER_THREADS) , mStarvationStartTimeMs (0 ) , mThreadPoolStarted (false ) , mThreadPoolSeq (1 ) , mCallRestriction (CallRestriction::NONE) { if (mDriverFD >= 0 ) { mVMStart = mmap (nullptr , BINDER_VM_SIZE, PROT_READ, MAP_PRIVATE | MAP_NORESERVE, mDriverFD, 0 ); ... }
首先通过 open_driver() 函数调用 open() 打开驱动,它会创建binder_proc对象,并将进程等相关信息保存到binder_proc对象中,并返回fd文件描述符,然后调用 mmap() 把内核空间虚拟内存和用户空间虚拟内存映射到同一块物理内存中;
其中 ProcessState 的成员变量 mDriverFD 记录 binder 驱动的 fd,用于访问 binder 设备;
open() 实际上调用的是 binder 驱动启动时注册的文件操作函数,在 kernel/drivers/staging/android/binder.c 中可以找到定义的 binder_fops 查看对应关系,
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 static const struct file_operations binder_fops = { .owner = THIS_MODULE, .poll = binder_poll, .unlocked_ioctl = binder_ioctl, .compat_ioctl = binder_ioctl, .mmap = binder_mmap, .open = binder_open, .flush = binder_flush, .release = binder_release, };
即 open 对应 binder_open,mmap 对应 binder_mmap,ioctl 对应 binder_ioctl;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 #define DEFAULT_MAX_BINDER_THREADS 15 static int open_driver (const char *driver) int fd = open (driver, O_RDWR | O_CLOEXEC); if (fd >= 0 ) { int vers = 0 ; status_t result = ioctl (fd, BINDER_VERSION, &vers); ... size_t maxThreads = DEFAULT_MAX_BINDER_THREADS; result = ioctl (fd, BINDER_SET_MAX_THREADS, &maxThreads); ... uint32_t enable = DEFAULT_ENABLE_ONEWAY_SPAM_DETECTION; result = ioctl (fd, BINDER_ENABLE_ONEWAY_SPAM_DETECTION, &enable); ... return fd; }
open_driver() 主要干了三件事:
调用 open 打开驱动,open 函数会经过系统调用,最终执行 binder 驱动程序中的 binder_open 函数;
调用 ioctl 获取 BINDER_VERSION;
调用 ioctl 设置当前进程最大的 Binder 线程数量,这里设置的线程数是 15 个(15 是 binder 非主线程的数量,还有个 binder 主线程,所以最大线程数是 15 +1 +其他没有调用 spawnPooledThread(),直接调用 joinThreadPool() 将当前线程直接加入 binder 线程队列的线程);
总结
通过 open_driver() 函数 调用 open() 打开驱动;
调用 mmap() 把内核空间虚拟内存和用户空间虚拟内存映射到同一块物理内存中(在 Android 11之前,SM 映射的虚拟内存分配空间是 128K,现在和普通应用一样都是 1M - 8K 了,在 BINDER_VM_SIZE 中定义);
1.2 设置上下文管理者 frameworks/native/libs/binder/ProcessState.cpp
becomeContextManager()
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 void ProcessState::becomeContextManager () AutoMutex _l(mLock); flat_binder_object obj { .flags = FLAT_BINDER_FLAG_TXN_SECURITY_CTX, }; status_t result = ioctl (mDriverFD, BINDER_SET_CONTEXT_MGR_EXT, &obj); if (result != 0 ) { android_errorWriteLog (0x534e4554 , "121035042" ); int unused = 0 ; result = ioctl (mDriverFD, BINDER_SET_CONTEXT_MGR, &unused); } if (result == -1 ) { ALOGE ("Binder ioctl to become context manager failed: %s\n" , strerror (errno)); } }
注册 servicemanager 为 binder 机制守护进程 ,其实就是把 0 号的 handler 给 servicemanager 使用,以后只要访问 0 号的 handler,binder 驱动就知道是与 servicemanager 进行交互。
Android 10 新增 BINDER_SET_CONTEXT_MGR_EXT 命令来设置安全的上下文管理者,如果设置失败,则传入原有的 BINDER_SET_CONTEXT_MGR 命令设置上下文管理者,两者区别在于是否携带参数;
1.3 进入循环 system/core/libutils/Looper.cpp
looper->pollAll()
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 int Looper::pollAll (int timeoutMillis, int * outFd, int * outEvents, void ** outData) if (timeoutMillis <= 0 ) { int result; do { result = pollOnce (timeoutMillis, outFd, outEvents, outData); } while (result == POLL_CALLBACK); return result; } else { ... for (;;) { int result = pollOnce (timeoutMillis, outFd, outEvents, outData); if (result != POLL_CALLBACK) { return result; } ... }
之前是 binder_loop() 死循环接收驱动的消息,现在通过 looper 监听 fd 来 handleEvent。
BinderCallback::setupTo(looper)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 class BinderCallback : public LooperCallback {public : static sp<BinderCallback> setupTo (const sp<Looper>& looper) sp<BinderCallback> cb = sp<BinderCallback>::make (); int binder_fd = -1 ; IPCThreadState::self ()->setupPolling (&binder_fd); LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL_IF (binder_fd < 0 , "Failed to setupPolling: %d" , binder_fd); int ret = looper->addFd (binder_fd, Looper::POLL_CALLBACK, Looper::EVENT_INPUT, cb, nullptr ); LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL_IF (ret != 1 , "Failed to add binder FD to Looper" ); return cb; } int handleEvent (int , int , void * ) override IPCThreadState::self ()->handlePolledCommands (); return 1 ; }
setupPolling(), flushCommands()
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 status_t IPCThreadState::setupPolling (int * fd) if (mProcess->mDriverFD < 0 ) { return -EBADF; } mOut.writeInt32 (BC_ENTER_LOOPER); flushCommands (); *fd = mProcess->mDriverFD; return 0 ; } void IPCThreadState::flushCommands () ... talkWithDriver (false ); ... }
setupPolling() 向 IPCThreadState.mOut(mOut 就是需要向驱动写入的数据,是一个 Parcel 对象) 中写入命令 BC_ENTER_LOOPER,然后将 BinderCallback 里面的 binder_fd 指向 open(“/dev/binder”) 是 binder 设备文件对应的 fd。
setupPolling() 和 flushCommands() 一起就是告诉 binder 驱动 sm 已经进入循环模式,可以处理数据了。addFd() 是 Looper 中的方法,实现是通过 epoll 机制监听 binder 对应的 fd,当可读时就会调用 handleEvent()。至此 sm 的准备工作完成,可以接收客户端的调用了。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 status_t IPCThreadState::handlePolledCommands () status_t result; do { result = getAndExecuteCommand (); } while (mIn.dataPosition () < mIn.dataSize ()); processPendingDerefs (); flushCommands (); return result; }
sm 通过 epoll 机制在 binder_fd 有变化时执行 handleEvent(),此方法调用了 handlePolledCommands(),这个方法是告诉 sm,binder 有数据可读,具体需要再次从 binder 读取。
此部分参考:参考1 ,参考2
2. 获取 servicemanager(native 层) 获取 servicemanager 的情况有两种:
注册服务到 sm 时:addService();
通过 sm 获取服务时:getService();
最终都会调用到 IServiceManager.cpp.defaultServiceManager()
frameworks/native/libs/binder/IServiceManager.cpp
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 sp<IServiceManager> defaultServiceManager () std::call_once (gSmOnce, []() { sp<AidlServiceManager> sm = nullptr ; while (sm == nullptr ) { sm = interface_cast <AidlServiceManager>(ProcessState::self ()->getContextObject (nullptr )); if (sm == nullptr ) { ALOGE ("Waiting 1s on context object on %s." , ProcessState::self ()->getDriverName ().c_str ()); sleep (1 ); } } gDefaultServiceManager = new ServiceManagerShim (sm); }); return gDefaultServiceManager; }
frameworks/native/libs/binder/ProcessState.cpp
2.1 ProcessState::self() 1 2 3 4 sp<ProcessState> ProcessState::self () return init (kDefaultDriver, false ); }
ProcessState::self() 和小结 1.1 一样,都是调用 init() 创建一个 ProcessState 对象,打开 binder 驱动,并调用 mmap() 把内核空间虚拟内存和用户空间虚拟内存映射到同一块物理内存中。
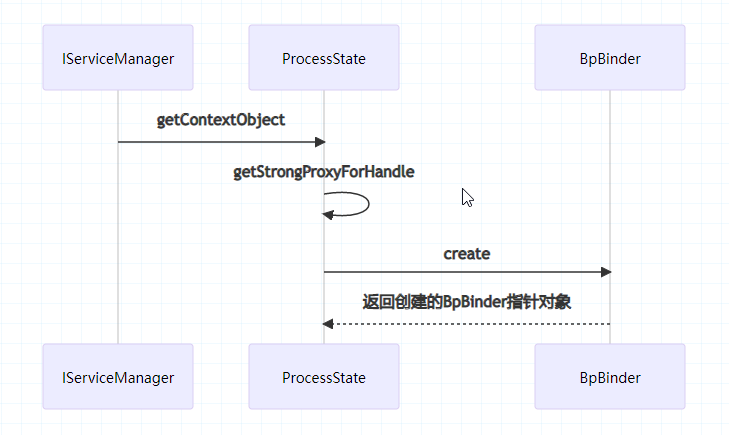
2.2 getContextObject() getContextObject() 函数调用
1 2 3 4 5 6 sp<IBinder> ProcessState::getContextObject (const sp<IBinder>& ) sp<IBinder> context = getStrongProxyForHandle (0 ); ... return context; }
获取 handle 值为 0 的对应代理对象,返回了一个 IBinder 对象;
getStrongProxyForHandle()
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 sp<IBinder> ProcessState::getStrongProxyForHandle (int32_t handle) sp<IBinder> result; AutoMutex _l(mLock); handle_entry* e = lookupHandleLocked (handle); if (e != nullptr ) { IBinder* b = e->binder; if (b == nullptr || !e->refs->attemptIncWeak (this )) { if (handle == 0 ) { IPCThreadState* ipc = IPCThreadState::self (); CallRestriction originalCallRestriction = ipc->getCallRestriction (); ipc->setCallRestriction (CallRestriction::NONE); Parcel data; status_t status = ipc->transact ( 0 , IBinder::PING_TRANSACTION, data, nullptr , 0 ); ipc->setCallRestriction (originalCallRestriction); if (status == DEAD_OBJECT) return nullptr ; }s sp<BpBinder> b = BpBinder::create (handle); e->binder = b.get (); if (b) e->refs = b->getWeakRefs (); result = b; } else { ... } return result; }
lookupHandleLocked() 函数作用是根据 handle 值来查找对应的 handle_entry,handle_entry 是一个结构体,里面记录 IBinder 和 weakref_type 两个指针。
所以 getContextObject() 的主要工作就是当 handle 值所对应的 IBinder 不存在或弱引用无效时会创建 BpBinder,否则直接获取 。 针对 handle==0 的特殊情况,通过 PING_TRANSACTION 来判断是否准备就绪。如果在 context manager 还未生效前,一个 BpBinder 的本地引用就已经被创建,那么驱动将无法提供 context manager 的引用。创建 BpBinder 对象中会将 handle 相对应 Binder 的弱引用增加 1。
2.3 interface_cast() frameworks/native/libs/binder/include/binder/IInterface.h
interface_cast()
1 2 3 4 5 template <typename INTERFACE>inline sp<INTERFACE> interface_cast (const sp<IBinder>& obj) return INTERFACE::asInterface (obj); }
interface_cast 是一个模板方法,针对于 interface_cast<AidlServiceManager>(BpBinder::create(0)); ,转换代码即为:
1 2 3 4 inline sp<AidlServiceManager> interface_cast (const sp<IBinder>& obj) return AidlServiceManager::asInterface (obj); }
AidlServiceManager 定义为:
1 using AidlServiceManager = android::os::IServiceManager;
也就是说,这个对象实际上就是 android::os::IServiceManager 对象,那么 asInterface() 函数定义在哪里呢?此处需要注意的是 :
在 IServiceManager.aidl 编译出来的 out/soong/.intermediates/frameworks/native/libs/binder/libbinder/android_arm64_armv8-a_shared/gen/aidl/android/os/IServiceManager.cpp 和 IServiceManager.h 头文件中可以看到如下代码:
1 2 3 4 DECLARE_META_INTERFACE (ServiceManager)DO_NOT_DIRECTLY_USE_ME_IMPLEMENT_META_INTERFACE (ServiceManager, "android.os.IServiceManager" )
而 Android 旧版本中会分别在 frameworks/native/libs/binder/include/binder/IServiceManager.h 和 frameworks/native/libs/binder/IServiceManager.cpp 中定义如上两行代码调用模板函数。
所以传入的 INTERFACE 就是 ServiceManager,对应的 IInterface.h 中的定义为:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 #define DECLARE_META_INTERFACE(INTERFACE) \ public: \ static const ::android::String16 descriptor; \ static ::android::sp<I##INTERFACE> asInterface( \ const ::android::sp<::android::IBinder> & obj); \ ... static const std::unique_ptr<I##INTERFACE>& getDefaultImpl ()
DECLARE_META_INTERFACE 部分只是声明,略过,接下来看实现部分(也是在 IInterface.h 中):
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 #define IMPLEMENT_META_INTERFACE(INTERFACE, NAME) \ DO_NOT_DIRECTLY_USE_ME_IMPLEMENT_META_INTERFACE(INTERFACE, NAME) \ #endif #define DO_NOT_DIRECTLY_USE_ME_IMPLEMENT_META_INTERFACE(INTERFACE, NAME)\ ... \ ::android::sp<I##INTERFACE> I##INTERFACE::asInterface( \ const ::android::sp<::android::IBinder> & obj) \ { \ ::android::sp<I##INTERFACE> intr; \ if (obj != nullptr) { \ intr = ::android::sp<I##INTERFACE> ::cast( \ obj->queryLocalInterface(I##INTERFACE::descriptor)); \ if (intr == nullptr) { \ intr = ::android::sp<Bp##INTERFACE> ::make(obj); \ } \ } \ return intr; \ }
把 ServiceManager 代入 INTERFACE:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 ::android::sp<IServiceManager> IServiceManager::asInterface ( \ const ::android::sp<::android::IBinder>& obj) \ ::android::sp<IServiceManager> intr; \ if (obj != nullptr ) { \ intr = ::android::sp<IServiceManager>::cast ( \ obj->queryLocalInterface (IServiceManager::descriptor)); \ if (intr == nullptr ) { \ intr = ::android::sp<BpServiceManager>::make (obj); \ } \ } \ return intr; \ }
obj 是 BpBinder,所以 interface_cast() 最后就是返回一个 BpServiceManager 对象 ,
Android 11 以前版本:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class BpServiceManager : public BpInterface<IServiceManager>{ public : explicit BpServiceManager (const sp<IBinder>& impl) : BpInterface<IServiceManager>(impl) { } virtual sp<IBinder> getService (const String16& name) const { ... } ... virtual status_t addService (const String16& name, const sp<IBinder>& service, bool allowIsolated, int dumpsysPriority) Parcel data, reply; data.writeInterfaceToken (IServiceManager::getInterfaceDescriptor ()); data.writeString16 (name); data.writeStrongBinder (service); data.writeInt32 (allowIsolated ? 1 : 0 ); data.writeInt32 (dumpsysPriority); status_t err = remote ()->transact (ADD_SERVICE_TRANSACTION, data, &reply); return err == NO_ERROR ? reply.readExceptionCode () : err; }
Android 11 开始版本:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 class BpServiceManager : public ::android::BpInterface<IServiceManager> {public : explicit BpServiceManager (const ::android::sp<::android::IBinder>& _aidl_impl) virtual ~BpServiceManager () = default ; ::android::binder::Status getService (const ::std::string& name, ::android::sp<::android::IBinder>* _aidl_return) override ; ... ::android::binder::Status addService (const ::std::string& name, const ::android::sp<::android::IBinder>& service, bool allowIsolated, int32_t dumpPriority) override ; ... };
看到 BpServiceManager 父类是 BpInterface,看一下 BpServiceManager 的构造函数:
1 2 3 4 5 public : explicit BpServiceManager (const sp<IBinder>& impl) : BpInterface<IServiceManager>(impl) { }
在构造函数的 初始化列表 中调用了基类的 BpInterface 的构造函数:
frameworks/native/libs/binder/include/binder/IInterface.h
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 template <typename INTERFACE>class BpInterface : public INTERFACE, public BpRefBase{ public : explicit BpInterface (const sp<IBinder>& remote) ... template <typename INTERFACE>inline BpInterface<INTERFACE>::BpInterface (const sp<IBinder>& remote) : BpRefBase (remote) { }
BpInterface 调用了基类 BpRefBase 的构造函数,该构造函数位于 Binder.cpp 中;
frameworks/native/libs/binder/include/binder/Binder.h
1 2 3 4 5 class BpRefBase : public virtual RefBase{ protected : explicit BpRefBase (const sp<IBinder>& o) virtual ~BpRefBase ();
看一下构造函数实现:
frameworks/native/libs/binder/Binder.cpp
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 BpRefBase::BpRefBase (const sp<IBinder>& o) : mRemote (o.get ()), mRefs (nullptr ), mState (0 ) { extendObjectLifetime (OBJECT_LIFETIME_WEAK); if (mRemote) { mRemote->incStrong (this ); mRefs = mRemote->createWeak (this ); } }
在 BpRefBase 的初始化列表中 mRemote(o.get()), 最终就是mRemote = new BpBinder(0),即 BpServiceManager 对象初始化过程中,比较重要工作的是类 BpRefBase 的 mRemote 指向小结 2.2 getContextObject() 的 BpBinder::create(0); ,从而 BpServiceManager 能够利用 Binder 进行通信。
2.4 ServiceManagerShim 在 defaultServiceManager 函数中,通过 new 的方式直接初始化一个 ServiceManagerShim 指针对象,
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 [[clang::no_destroy]] static sp<IServiceManager> gDefaultServiceManager; sp<IServiceManager> defaultServiceManager () std::call_once (gSmOnce, []() { sp<AidlServiceManager> sm = nullptr ; while (sm == nullptr ) { sm = interface_cast <AidlServiceManager>(ProcessState::self ()->getContextObject (nullptr )); ... gDefaultServiceManager = new ServiceManagerShim (sm); ... }
看一下 ServiceManagerShim 的定义:
1 2 3 4 5 6 class ServiceManagerShim : public IServiceManager{ public : explicit ServiceManagerShim (const sp<AidlServiceManager>& impl)
注意 :此处的父类 IServiceManager 并非 frameworks/native/libs/binder/IServiceManager.cpp ,和小结 2.3 所述一样,应该是 namespace 为 android::os::IServiceManager 的 frameworks/native/libs/binder/aidl/android/os/IServiceManager.aidl 生成的 IServiceManager.cpp;
再来看一下 ServiceManagerShim 的构造函数:
1 2 3 4 ServiceManagerShim::ServiceManagerShim (const sp<AidlServiceManager>& impl) : mTheRealServiceManager (impl) {}
mTheRealServiceManager 也是 android::os::IServiceManager 类型的实例,也是在 IServiceManager.aidl 生成的 IServiceManager.cpp 中定义的,
1 2 protected : sp<AidlServiceManager> mTheRealServiceManager;
可以看出 mTheRealServiceManager 就是一个 AidlServiceManager 实例,并且在 ServiceManagerShim 实例化时赋值;
那么 ServiceManagerShim 什么时候实例化呢?是在文中所述的 defaultServiceManager() 中:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 sp<IServiceManager> defaultServiceManager () ... sm = interface_cast <AidlServiceManager>(ProcessState::self ()->getContextObject (nullptr )); ... gDefaultServiceManager = sp<ServiceManagerShim>::make (sm); ... }
从小结 2.3 可知,此处的 sm 相当于 new BpServiceManager(new BpBinder(0)),因此可知,在最终返回的这个 ServiceManagerShim 对象中,有一个指针参数 mTheRealServiceManager 是指向 new BpServiceManager(new BpBinder(0)) 的;
1 2 3 4 ServiceManagerShim::ServiceManagerShim (const sp<AidlServiceManager>& impl) : mTheRealServiceManager (impl) {}
2.4 总结 ProcessState::self() 主要工作:
调用 init() 创建一个 ProcessState 对象;
在 ProcessState 构造函数中调用 open() 打开 binder 驱动;
调用 mmap() 把内核空间虚拟内存和用户空间虚拟内存映射到同一块物理内存中;
设置当前进程最大的 Binder 线程数量 为 15;
getContextObject() 主要工作:
当 handle 值(此处值为 0)所对应的 IBinder 不存在或弱引用无效时会创建 BpBinder,否则直接获取;
interface_cast() 主要工作:
返回一个 BpServiceManager 对象;
BpServiceManager 通过继承接口 IServiceManager 实现了接口中的业务逻辑函数;
通过成员变量mRemote= new BpBinder(0) 进行 Binder 通信工作;
BpBinder 通过 handler 来指向所对应 BBinder, 在整个 Binder 系统中 handle=0 代表 ServiceManager 所对应的 BBinder;
ServiceManagerShim() 主要工作:
有一个指针参数 mTheRealServiceManager 指向 BpServiceManager;
defaultServiceManager 函数主要:
返回一个 ServiceManagerShim 对象指针,这个对象指针继承自 android::IServiceManager;
这个 ServiceManagerShim 对象指针中,有一个指针参数 mTheRealServiceManager ,其实质是一个 aidl 对象android::os::IServiceManager 对象,此处是 BpServiceManager 对象指针;
BpServiceManager 对象指针初始化的时候,是以 new BpBinder(0) 为参数的,在 BpServiceManager 对象中表现为一个 mRemote 指针对象;